What Builds New Strands Of Dna
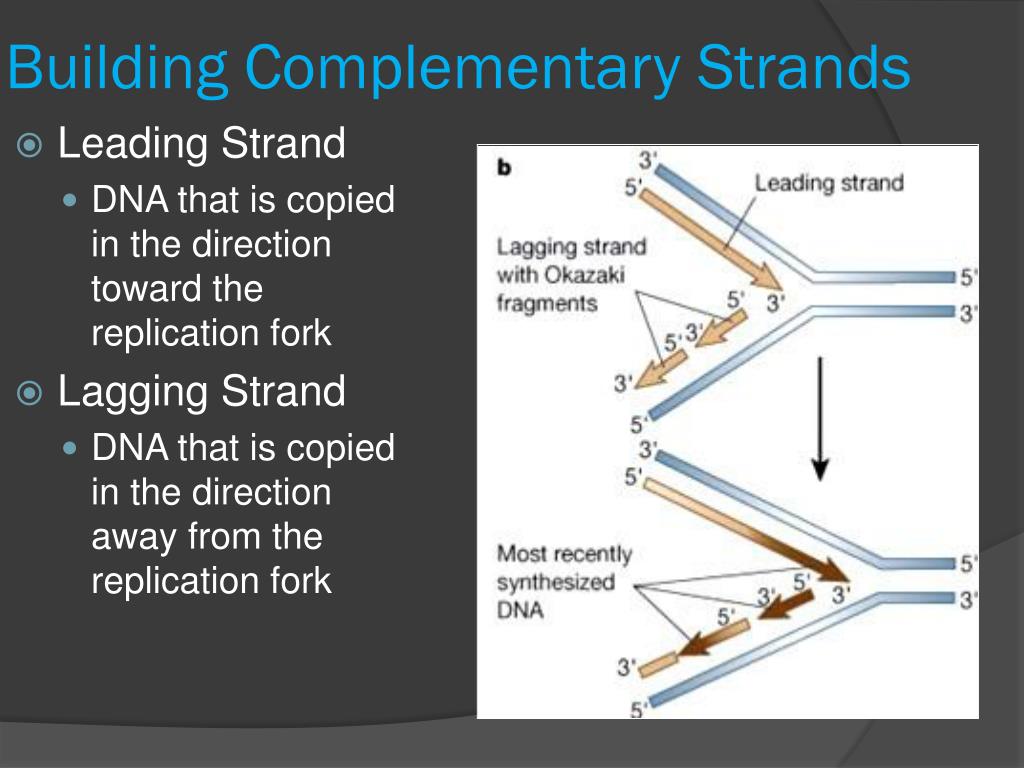
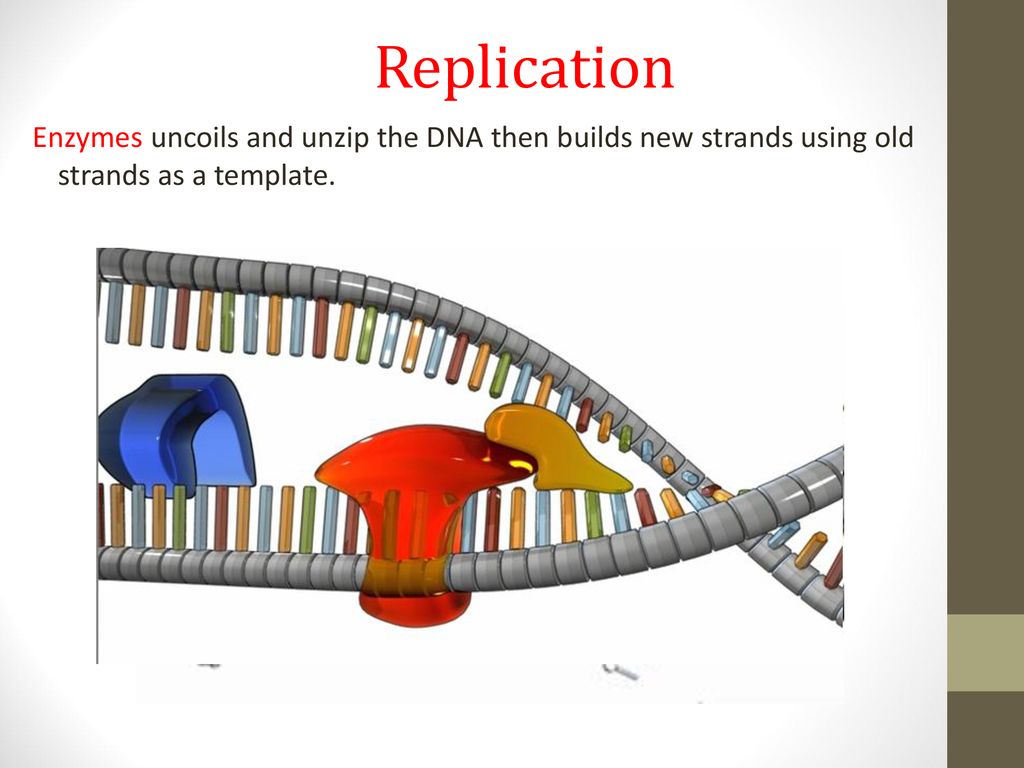
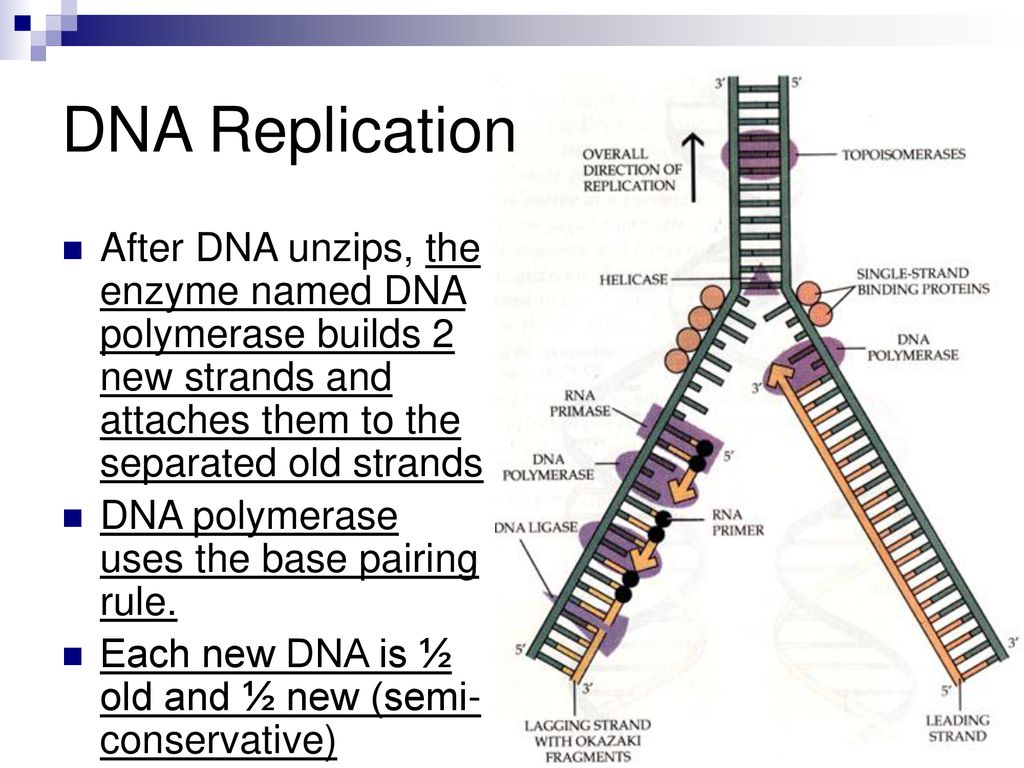
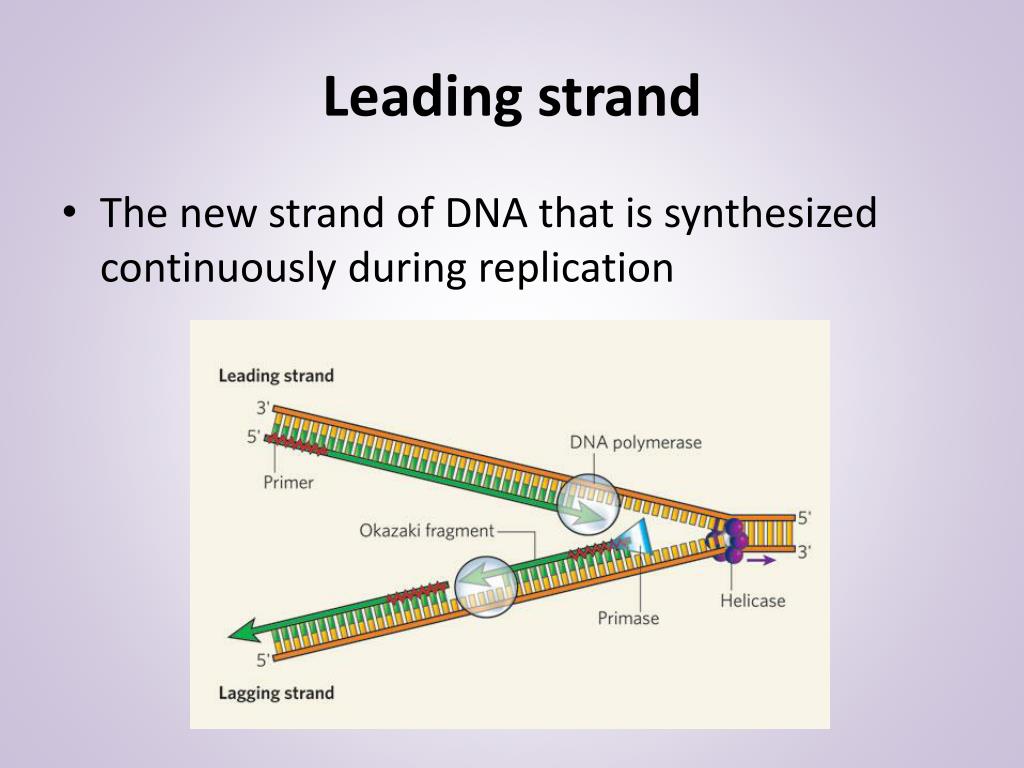
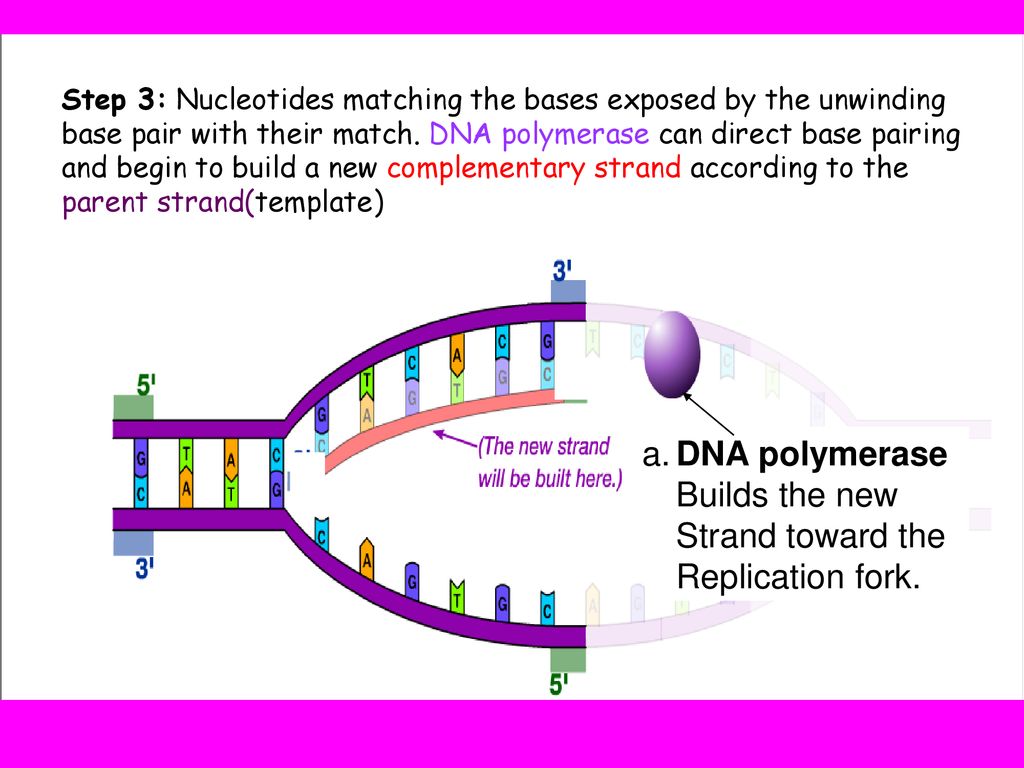
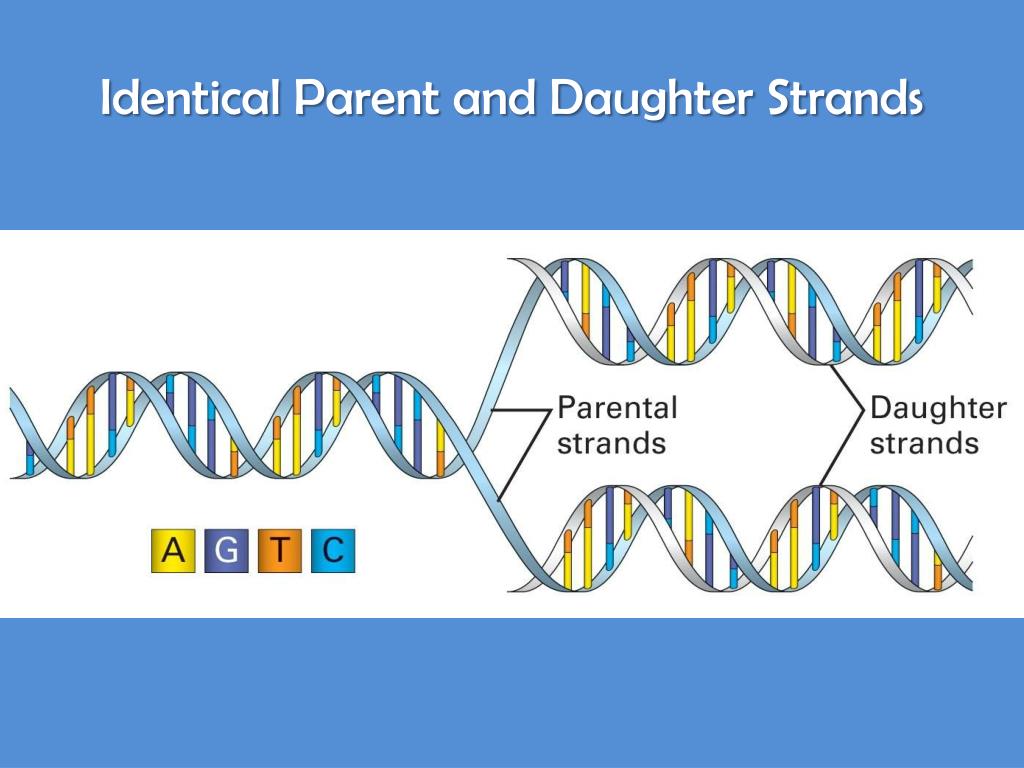
What Builds New Strands Of Dna - At a replication fork, the dna of both new daughter strands is synthesized by a multienzyme complex that contains the dna polymerase. Dna polymerase is a remarkable enzyme that plays a central role in the synthesis of new dna strands. A phosphate group, a sugar group and one of four types of nitrogen. They are about 1000 nucleotides long. The process of dna replication involves the synthesis of new strands, which are categorized into leading and lagging strands. They ensure when cells divide, each new cell gets a complete copy of. Northwestern medicine scientists have discovered new details about how the human genome produces instructions for creating proteins and cells, the building blocks of life,. Dna polymerase iii catalyzes the reaction by which a new nucleotide is added to a growing dna strand. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. Within eukaryotes, dna replication is controlled within the context of the cell cycle. The lagging strand is replicated in fragment known as okazaki fragments; They are about 1000 nucleotides long. Dna replication takes place during the s phase (synthesis phase). A phosphate group, a sugar group and one of four types of nitrogen. Dna polymerase plays a pivotal role by adding nucleotides to the growing dna strand in a sequence complementary to the template strand. Proteins, which are essential cellular building blocks and mediators, are built using instructions contained in. These building blocks are made of three parts: Progression through checkpoints is controlled through complex i… It does this by adding dna nucleotides one at a time. These strands differ in the manner and direction. That reaction is seen in figure \(\pageindex{2}\). Progression through checkpoints is controlled through complex i… Dna polymerase controls the addition of dna nucleotides to the new strand of dna. Chromosomes are tightly coiled structures in each of your cells that contain dna, the code for all life. The lagging strand is replicated in fragment known as okazaki fragments; These building blocks are made of three parts: It requires a primer, a short rna. The model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is. Dna polymerase plays a pivotal role by adding nucleotides to the growing dna strand. That reaction is seen in figure \(\pageindex{2}\). Within eukaryotes, dna replication is controlled within the context of the cell cycle. The progress of the eukaryotic cell through the cycle is controlled by cell cycle checkpoints. Dna polymerase iii catalyzes the reaction by which a new nucleotide is added to a growing dna strand. The okazaki fragments are knitted together by. One class of proteins required for replication binds to dna polymerases, increasing the activity of the polymerases and causing them to remain bound to the template dna so that they continue. Dna polymerase is an enzyme that builds new strands of dna. A phosphate group, a sugar group and one of four types of nitrogen. They are about 1000 nucleotides. The progress of the eukaryotic cell through the cycle is controlled by cell cycle checkpoints. The process of dna replication involves the synthesis of new strands, which are categorized into leading and lagging strands. They are about 1000 nucleotides long. Two replication forks moving in opposite. As the cell grows and divides, it progresses through stages in the cell cycle; Each nucleotide consists of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. It requires a primer, a short rna. It does this by adding dna nucleotides one at a time. Two replication forks moving in opposite. Dna is made of chemical building blocks called nucleotides. An enzyme called ‘dna polymerase’ drives the process of building a new strand of dna. It does this by adding dna nucleotides one at a time. That reaction is seen in figure \(\pageindex{2}\). Dna polymerase iii catalyzes the reaction by which a new nucleotide is added to a growing dna strand. Dna polymerase is a remarkable enzyme that plays a. The okazaki fragments are knitted together by dna ligase. The dna remains one continuous strand by linking the dna fragments with dna ligase. The model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is. The process of dna replication involves. It does this by adding dna nucleotides one at a time. Dna polymerase plays a pivotal role by adding nucleotides to the growing dna strand in a sequence complementary to the template strand. Two replication forks moving in opposite. Which of the following builds new strands of dna? A phosphate group, a sugar group and one of four types of. Dna polymerase is an enzyme that builds new strands of dna. These strands differ in the manner and direction. Progression through checkpoints is controlled through complex i… As the cell grows and divides, it progresses through stages in the cell cycle; Within eukaryotes, dna replication is controlled within the context of the cell cycle. Which of the following builds new strands of dna? These strands differ in the manner and direction. New dna strands are built using nucleotides, which are the building blocks of dna. Below is a summary table of the major enzymes. Dna polymerase controls the addition of dna nucleotides to the new strand of dna. They are about 1000 nucleotides long. The okazaki fragments are knitted together by dna ligase. It requires a primer, a short rna. As the cell grows and divides, it progresses through stages in the cell cycle; Dna polymerase plays a pivotal role by adding nucleotides to the growing dna strand in a sequence complementary to the template strand. The rna primers are replaced with dna nucleotides; The lagging strand is replicated in fragment known as okazaki fragments; The dna remains one continuous strand by linking the dna fragments with dna ligase. The model for dna replication suggests that the two strands of the double helix separate during replication, and each strand serves as a template from which the new complementary strand is. Two replication forks moving in opposite. Its primary function is to add nucleotides to a growing dna chain,.PPT DNA Hereditary Molecules of Life PowerPoint Presentation, free
14.5 DNA Replication in Prokaryotes Biology LibreTexts
DNA, RNA & Protein Synthesis ppt download
The Structure of DNA by Ron Vale
DNA Replication Objective ppt download
PPT DNA Replication PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6899779
DNA Structure Visual.ly
Chapter 122 DNA Replication and Chromosomes ppt download
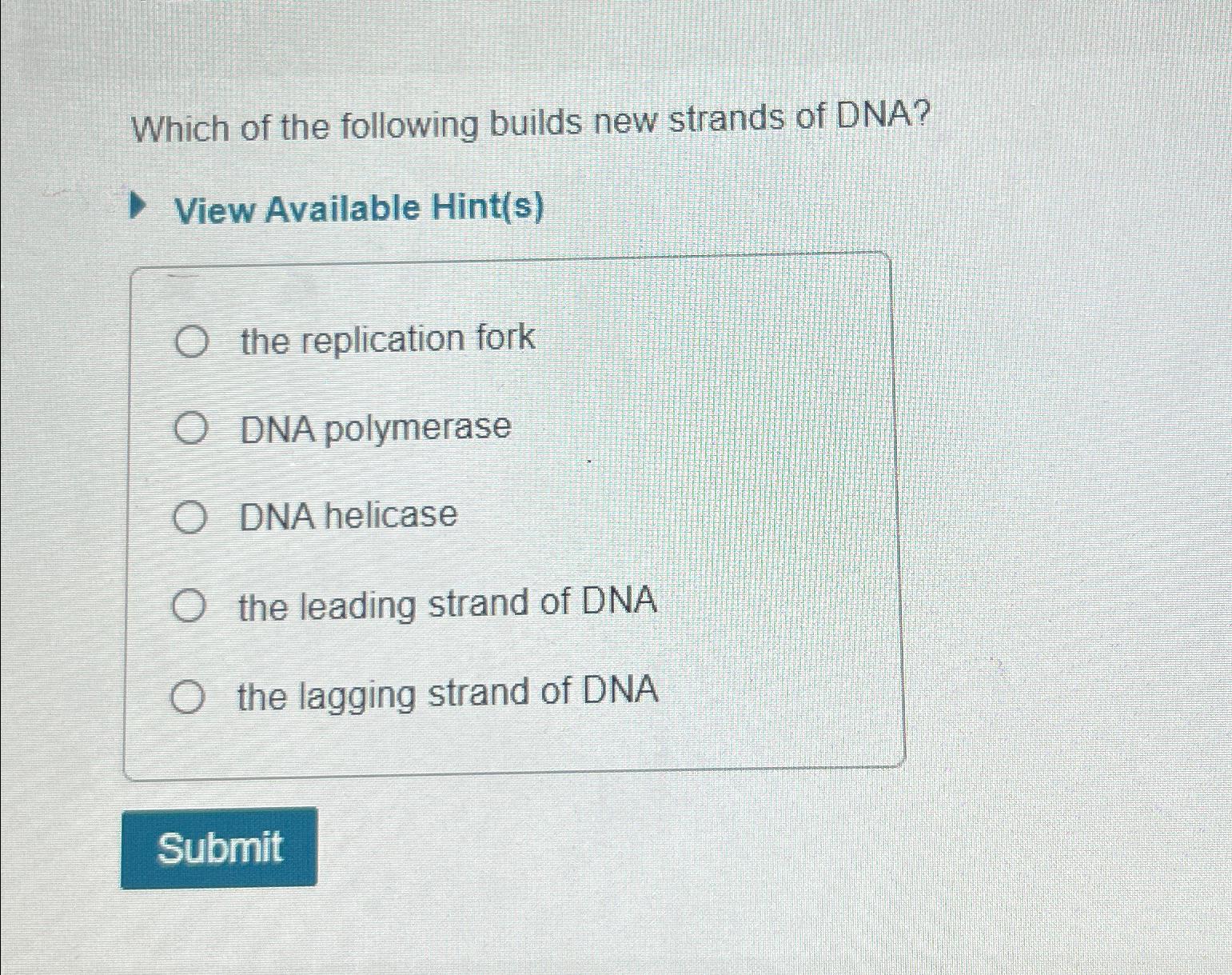
Solved Which of the following builds new strands of DNA?View
PPT DNA Replication PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2474510
Chromosomes Are Tightly Coiled Structures In Each Of Your Cells That Contain Dna, The Code For All Life.
Dna Polymerase Is An Enzyme That Builds New Strands Of Dna.
Northwestern Medicine Scientists Have Discovered New Details About How The Human Genome Produces Instructions For Creating Proteins And Cells, The Building Blocks Of Life,.
A Phosphate Group, A Sugar Group And One Of Four Types Of Nitrogen.
Related Post: