What Enzyme Builds New Dna Strands
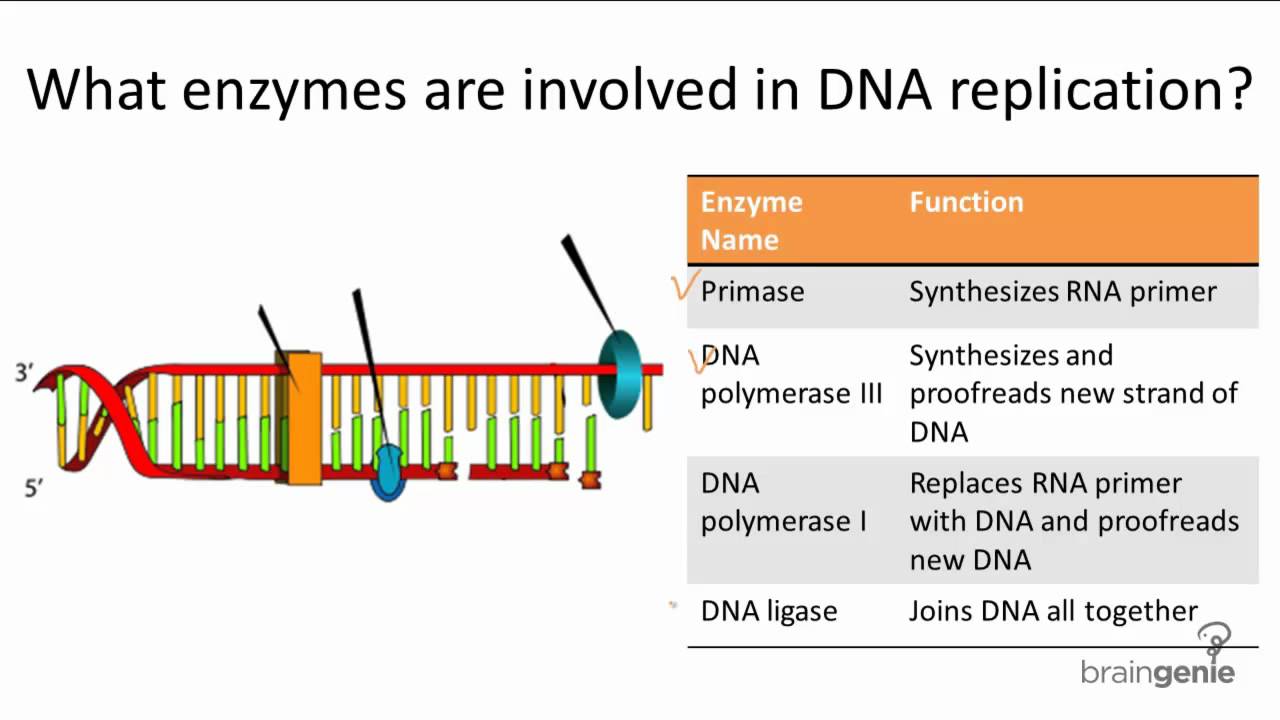
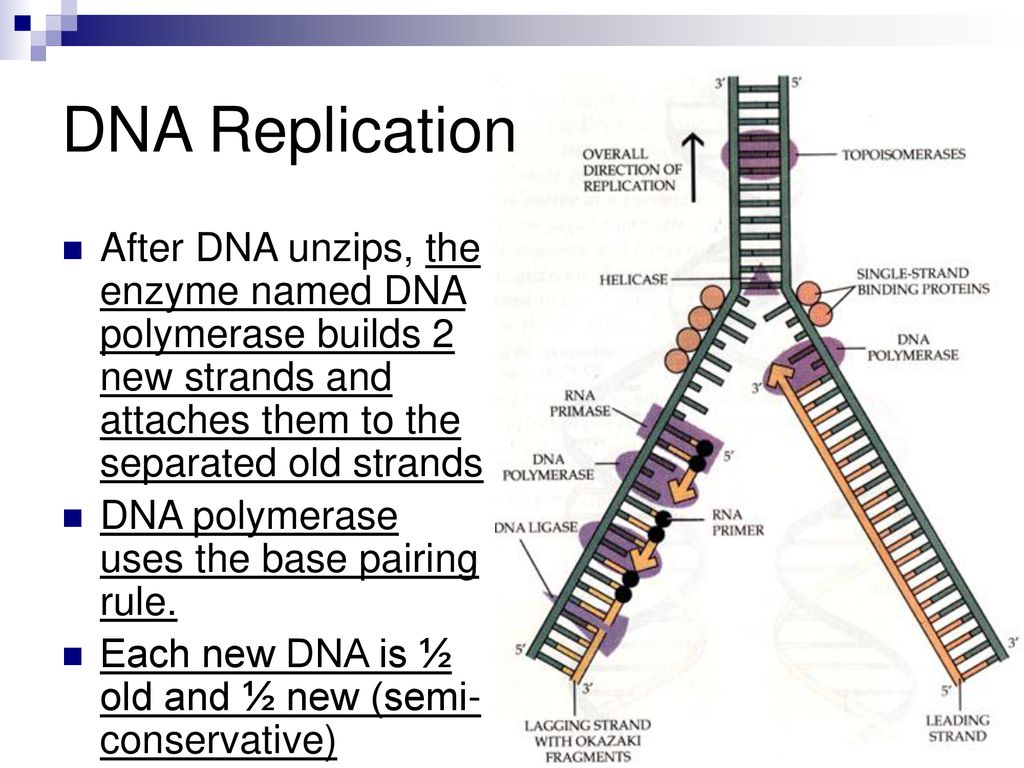
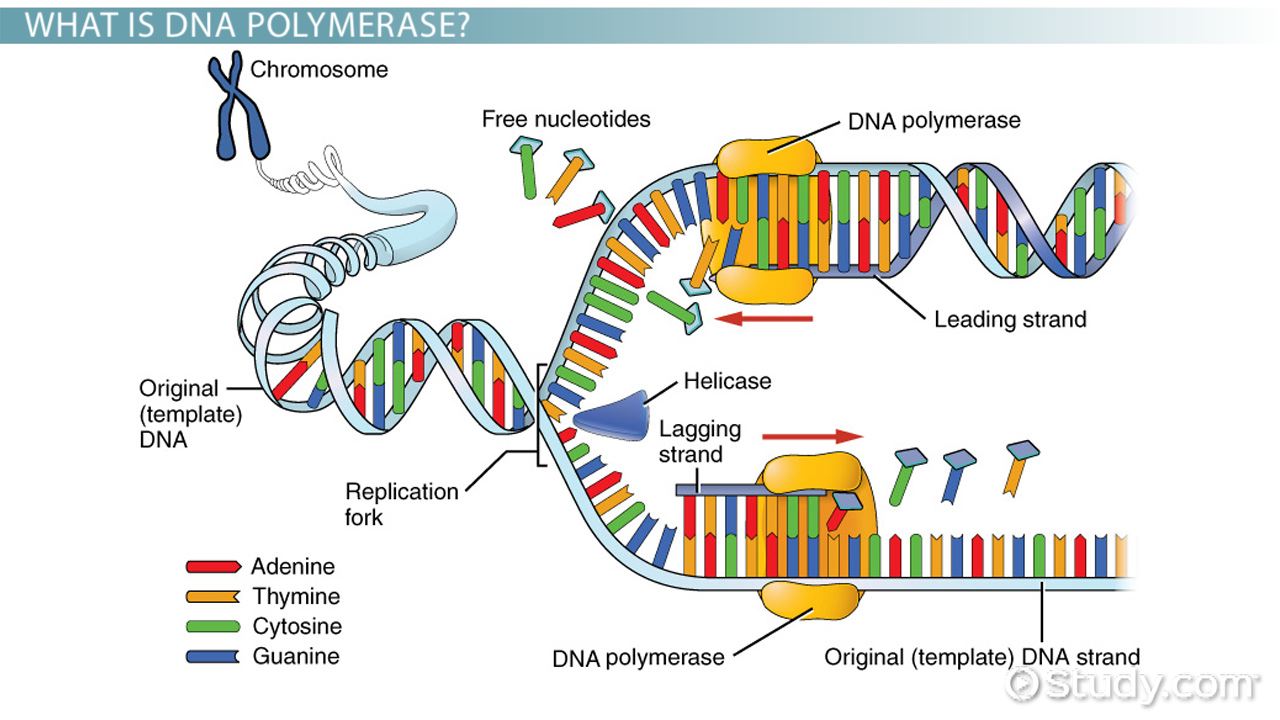
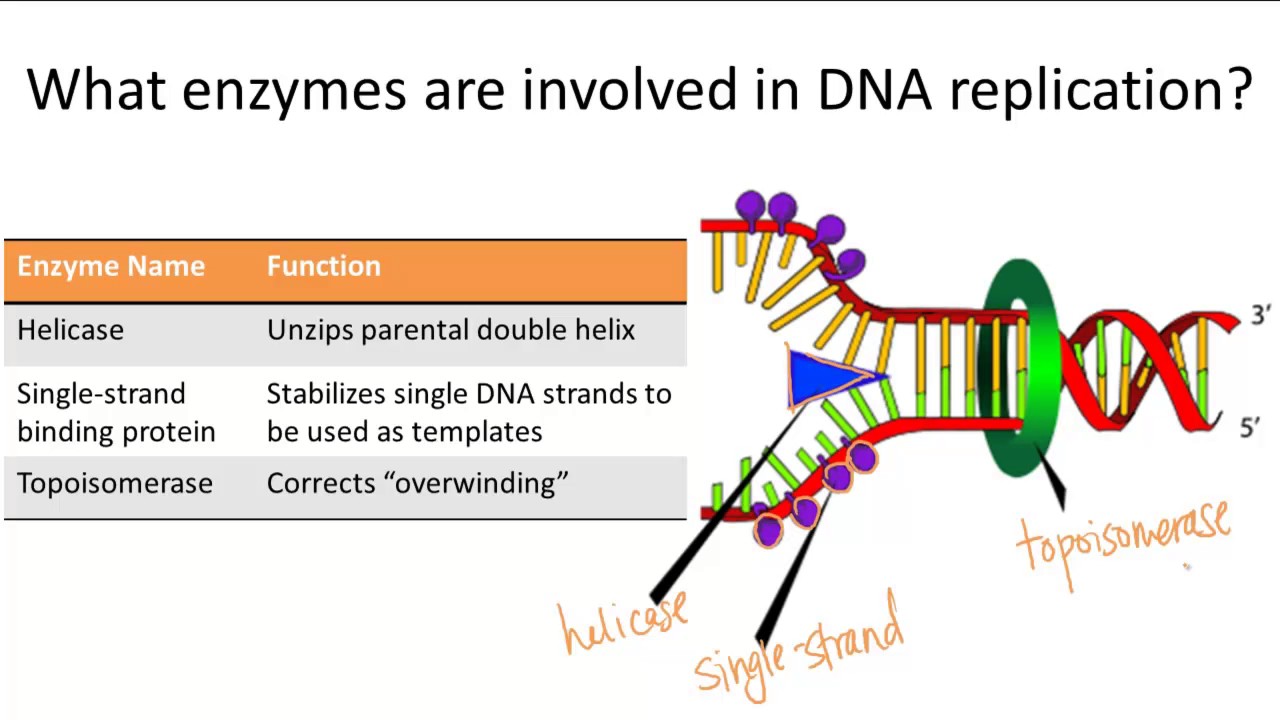
What Enzyme Builds New Dna Strands - The enzyme that builds a new dna strand during dna replication. First, the enzyme attaches to a strand of dna template and. “okazaki fragments” are short stretches of. Ribonucleotide reductase (rnr) is an enzyme that converts rna into dna for synthesis and repair. Dna polymerase iii is responsible for adding new nucleotides to the strand being synthesised. Below is a summary table of the major enzymes. The rna primers are replaced with dna nucleotides; Here are some of the key enzymes involved in dna replication: The rna primers are replaced with dna nucleotides; What are the four main enzymes involved in dna replication? There are two types of these enzymes: The four main enzymes involved in dna replication are dna helicase, rna primase, dna polymerase, and. Below is a summary table of. They have molecular weight 300,000, which contains six identical subunits. The dna remains one continuous strand by linking the dna fragments with dna ligase. Dna helicase enzyme functions “unwinds dna”. Ribonucleotide reductase (rnr) is an enzyme that converts rna into dna for synthesis and repair. Dna polymerase iii is responsible for adding new nucleotides to the strand being synthesised. The dna remains one continuous strand by linking the dna fragments with dna ligase. Dna has an antiparallel, double helix structure composed of two, complementary polynucleotide strands, held together. What are the four main enzymes involved in dna replication? Mit biochemists have visualized the enzyme's active state and observed. Below is a summary table of. They have molecular weight 300,000, which contains six identical subunits. Initially, an enzyme known as a helicase acts on the molecule of dna. Dna has an antiparallel, double helix structure composed of two, complementary polynucleotide strands, held together. Dna helicase enzyme functions “unwinds dna”. Dna polymerases are essential enzymes that synthesize new dna strands during replication, always extending from the 5' to 3' direction. Dna polymerases are indispensable enzymes in the dna replication process, responsible for synthesizing new dna strands by adding nucleotides. The dna remains one continuous strand by linking the dna fragments with dna ligase. Dna polymerase is the workhorse of the dna replication process, responsible for synthesizing new dna strands by adding nucleotides to the growing chain. Initially, an enzyme known as a helicase acts on the molecule of dna. “okazaki fragments” are short stretches of. Also involved in dna. Below is a summary table of the major enzymes. Dna polymerase iii is responsible for adding new nucleotides to the strand being synthesised. Dna polymerase is the workhorse of the dna replication process, responsible for synthesizing new dna strands by adding nucleotides to the growing chain. Ribonucleotide reductase (rnr) is an enzyme that converts rna into dna for synthesis and. The four main enzymes involved in dna replication are dna helicase, rna primase, dna polymerase, and. The dna remains one continuous strand by linking the dna fragments with dna ligase. The dna strand that dna polymerase constructs in the 5’ → 3’ direction. Dna has an antiparallel, double helix structure composed of two, complementary polynucleotide strands, held together. What are. Dna polymerase iii is responsible for adding new nucleotides to the strand being synthesised. The dna remains one continuous strand by linking the dna fragments with dna ligase. They have molecular weight 300,000, which contains six identical subunits. The rna primers are replaced with dna nucleotides; The four main enzymes involved in dna replication are dna helicase, rna primase, dna. Also involved in dna replication are dna polymerase i which replaces primers. Here are some of the key enzymes involved in dna replication: This problem is solved by topoisomerases, enzymes that catalyze the reversible breakage and rejoining of dna strands. The dna remains one continuous strand by linking the dna fragments with dna ligase. Mit biochemists have visualized the enzyme's. Dna helicase enzyme functions “unwinds dna”. Dna polymerase is the workhorse of the dna replication process, responsible for synthesizing new dna strands by adding nucleotides to the growing chain. “okazaki fragments” are short stretches of. This problem is solved by topoisomerases, enzymes that catalyze the reversible breakage and rejoining of dna strands. First, the enzyme attaches to a strand of. The rna primers are replaced with dna nucleotides; Here are some of the key enzymes involved in dna replication: The dna strand that dna polymerase constructs in the 5’ → 3’ direction. Below is a summary table of the major enzymes. Mit biochemists have visualized the enzyme's active state and observed. The enzyme that builds a new dna strand during dna replication. The dna remains one continuous strand by linking the dna fragments with dna ligase. The dna strand that dna polymerase constructs in the 5’ → 3’ direction. First, the enzyme attaches to a strand of dna template and. Dna has an antiparallel, double helix structure composed of two, complementary. Initially, an enzyme known as a helicase acts on the molecule of dna. There are two types of these enzymes: In prokaryotes, dna polymerase iii is the primary. Dna polymerase iii is responsible for adding new nucleotides to the strand being synthesised. Below is a summary table of. Dna helicase enzyme functions “unwinds dna”. Mit biochemists have visualized the enzyme's active state and observed. Also involved in dna replication are dna polymerase i which replaces primers. The rna primers are replaced with dna nucleotides; Dna polymerases are indispensable enzymes in the dna replication process, responsible for synthesizing new dna strands by adding nucleotides to a growing chain. This problem is solved by topoisomerases, enzymes that catalyze the reversible breakage and rejoining of dna strands. The rna primers are replaced with dna nucleotides; Dna polymerase is the workhorse of the dna replication process, responsible for synthesizing new dna strands by adding nucleotides to the growing chain. The dna remains one continuous strand by linking the dna fragments with dna ligase. Ribonucleotide reductase (rnr) is an enzyme that converts rna into dna for synthesis and repair. The dna remains one continuous strand by linking the dna fragments with dna ligase.DeoxyriboNucleic Acid ppt download
Dna Replication Diagram With Enzymes
DNA Replication Objective ppt download
Enzymes of DNA replication innocent tutor
The model represents DNA replication. What does enzyme 2 do? A. It
Enzymes Involved in DNA Replication YouTube
Enzyme That Joins The Dna Fragments Together
DNA, RNA & Protein Synthesis ppt download
DNA. Structure and Replication Presentation Biology
Dna Polymerase Enzyme Syntheses Labeled Educational Stock Vector
The Enzyme That Builds A New Dna Strand During Dna Replication.
What Are The Four Main Enzymes Involved In Dna Replication?
First, The Enzyme Attaches To A Strand Of Dna Template And.
The Four Main Enzymes Involved In Dna Replication Are Dna Helicase, Rna Primase, Dna Polymerase, And.
Related Post:


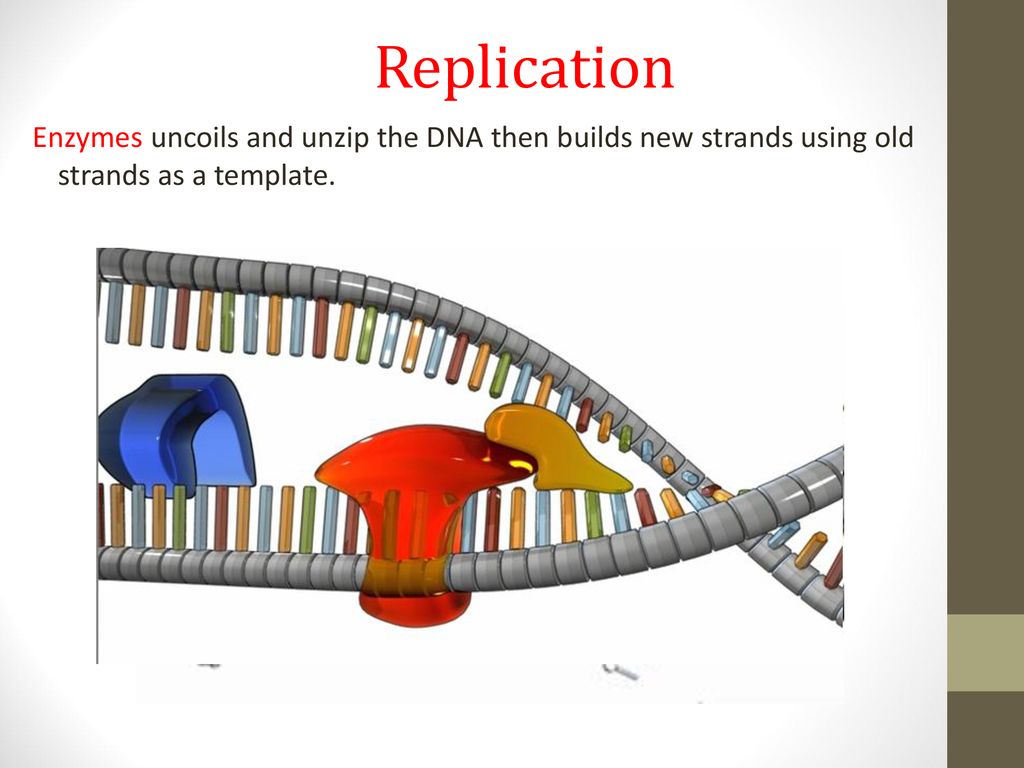
.PNG)
